- Visibility 556 Views
- Downloads 85 Downloads
- Permissions
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijos.2024.054
-
CrossMark
- Citation
A prospective study to compare the outcome of patellar fractures treated with tension band wiring versus cannulated cancellous screws fixation
Abstract
Background: The largest sesamoid bone in the body, the patella, is essential to the stability and functionality of the knee. It functions as a fulcrum to adhere to the patellar ligament and quadriceps tendon, increasing the quadriceps' effectiveness. Both static elements (ligaments and the joint capsule) and dynamic elements (muscles such as the hamstrings and quadriceps) are necessary for patella-femoral stability. Both direct trauma and indirect causes, such as falling when your quadriceps are clenched, can result in fractures. While direct blows might result in comminution and soft tissue injury, indirect injuries usually cause damage to the tendons or bones.There are different ways to treat fractures. For fractures with less than 2 mm displacement, non-operative treatments can be used. Surgical alternatives include screw fixation, tension band wiring and partial or complete patellectomy.
Aims and objectives: It is a comparative randomized control trial. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the cannulated cancellous screws techniques in terms of safety and outcome when compare to tension band wiring for treatment of displaced transverse patellar fractures.
Materials and Methods: A longitudinal observational study was carried out in the department of orthopaedics for a time period of 20 months from November 2020 to June 2022. Patients were divided into two groups one treated with cannulated cancellous screws and another treated with tension band wiring then followed up at intervals of 1st, 3rd and 6th month Results were evaluated with regard to union rate, ROM, pain score, functional outcome, complications and hardware removal rates.
Results: The mean radiological union was 9.2 weeks in cannulated cancellous screws group and 9.73 weeks in tension band wiring group, The mean knee ROM was 135° in cannulated cancellous screws Group and 129° in tension band wiring group and functional score in cannulated cancellous screws group was 66.7% excellent, 26.6% good and 6.7% poor outcomes. In tension band wiring group functional score was 46.6% excellent, 40% good and 13.4% poor outcomes as per WEST’S Criteria. Complications encountered in tension band wiring group were more with respect to hardware prominence, soft tissue irritation and hardware removal rates than cannulated cancellous screws group.
Conclusion: Cannulated cancellous screws for treatment of displaced transverse patella fracture are safe and biomechanically stable implant with lesser degree of soft tissue irritation when compared to tension band wiring.
Introduction
The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the human body, serves as the attachment site for both the quadriceps femoris tendon and patellar ligament. Within this tendon, patella is located in anterior aspect of the knee joint.[1] Patella-femoral joint stability is always dependent on static and dynamic soft tissue components, due to shallow and uneven fit between patella and trochlea. Ligaments, capsule of knee joint and tendon(patellar tendon) all contribute to static stability (MPFL). Dynamically, quadriceps femoris muscle, pes anserine group of muscles and biceps femoris muscle all contribute to patellar alignment through their contractile properties. Patella mainly functions to improve the efficiency of quadriceps muscle by acting as a fulcrum, to enhance the moment arm of extensor mechanism of knee.[1]
There are direct and indirect mechanisms that might cause patella fractures. Falling on your feet as your quadriceps are contracted eccentrically is the traditional indirect technique. The extensor mechanism fails when the force of a fall exceeds the knee's ability to resist flexion. The bone will break or the tendons will tear depending on how quickly the force is applied. A direct strike, on the other hand, is more likely to cause comminution, articular destruction, anterior soft tissue damage and therefore open injury. A direct impact coupled with knee flexion and quadriceps contraction can significantly shift fragments and injure soft tissues. Combinations of patterns are prevalent.[2]
Treatment options are non-operative and operative. Non-operative treatment is suitable for fractures with less than 2mm of displacement. Operative treatment includes Circumferentiallwireloop fixation , Magnusson wiring, Lotke longitudinal anterior band wiring ,Tension band wiring(TBW) ,Screws fixation with Tension band wiring(TBW),Partial patellectomy and Patellectomy. Complications include loss of knee range of motion, loss of reduction, infections, delayed union or non-union, osteoarthritis in patella-femoral joint.[3]
Hung et al., in 1985, used tension band principle by different methods; He found better results in stable fracture, although he found minor complications like wire breakage and k-wire protrusion in some patients.[4] In a cadaver model, Carpenter et al., in 1997 analysed three techniques for fixing transverse patella fractures. In comparison to screw fixation alone and tension band wiring alone, they found that screw fixation combined with anterior tension band delivered higher stability.[5] Chang et al., studies in 2011, also showed good results with cannulated cancellous screws for displaced transverse fracture of patella with lesser degree of hardware-related complications.[6] Adjal, J et al. and others in 2021 studied on the suture tension band fixation technique as an alternative treatment for patella fractures that may reduce the rate of prominent implants.[7]
Aims and Objectives
To compare the functional outcome of patellar fractures treated with Tension band wiring(TBW) versus Cannulated cancellous screw(CCS) fixation.
To observe rigid fixation and early mobilization that occurs after surgery
To observe the patient compliance and complications that may occur with the procedure
Materials & Methods
It is a Prospective comparative study conducted at Department of Orthopaedics, Narayana Medical College, Nellore. In the period of 20 months (November 2020 to June 2022). On study group of 30 (15+15) patients divided into two groups.
Detailed description of the groups
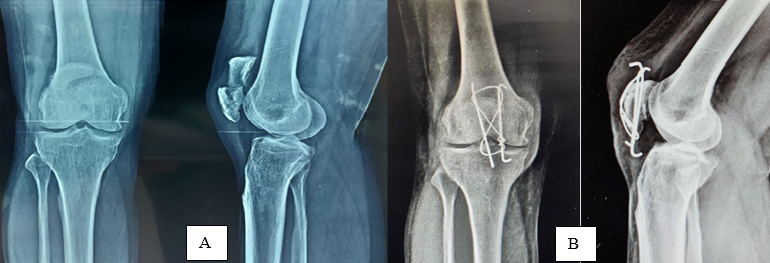
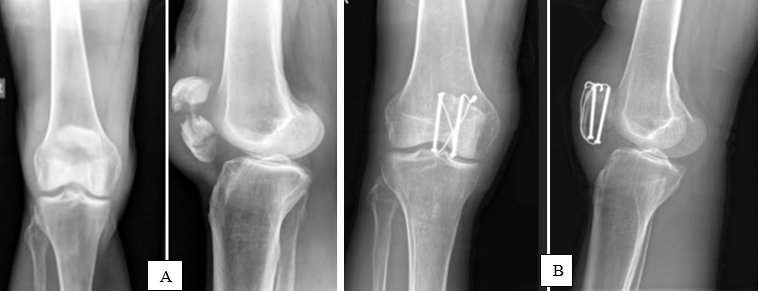
Patients who sustained transverse type of patella fracture, patients who fulfil the inclusion criteria are taken in our study. Patients who came evenly in the order were allotted for Cannulated cancellous screws ([Figure 2]A) technique and who came odd were allotted for Tension band wiring ([Figure 1]A) technique.
Inclusion criteria
In this study patients of age 18-80 years, patients medically fit for surgery having Closed type of fractures, transverse type of fracture and Patients giving informed consent were included.
Exclusion criteria
In this study patients with age less than 18 years and more than 80 years, patients with history of ongoing infection, All type of fractures except the transverse type, Patients not medically fit for surgery and Patients who are not wiling to provide informed consent were excluded.
Techniques of surgical fixation
A midline vertical skin incision of approximately 8icm was given. The subcutaneous tissue was incised and reflected outside for exposure of the anterior surface of the patella. Fractured patellar fragments were reduced nearly in anatomical position with the help of pointed bone holding forceps. Articular reduction was confirmed by palpating through the rent made through retinaculum medially or laterally.
In the tension band wiring (TBW) group, two Kirschner-wires were drilled vertically, 90 degrees to the fracture of patella through anterior half of patella & an 18 gauge stainless steel wire was passed behind the kirschner-wires with cuff of quadriceps femoris tendon and patellar tendon at bone tendon junction and tensioned in figure of eight manner to secure reduction. The knots of steel wire was placed superomedially or superolaterally, then stability of reduction was checked by flexion of knee joint. If the reduction was satisfactory superior end of kirschner-wires were bent and buried under the soft tissue close to superior pole of patella. Kirschner wires were cut and trimmed inferiorly to be buried under patellar tendon ([Figure 1]B).[4]
In the Cannulated Cancellous Screw group, first two kirschner wires were inserted in the mid-coronal plane perpendicular to fracture site under fluoroscopic guidance then replaced with two cannulated screw guide pins along the same tract in order to prevent inadvertent bending of this guide wire. Then we drilled along the guide wire with an appropriate cannulated drill bit and a partially threaded 4.0-mm cannulated cancellous screw was inserted along the guide wire making sure threaded part of screw that has crossed the fracture site either from superior or inferior pole of the patella based on site of fracture. The screw head was placed proud to the patellar cortex and threaded tip of the screw should be embedded within the patella. For second screw same procedure was followed and a 18 gauge stainless steel(SS) wire was negotiated along the guide wire tract in order to pass the SS wire inside the screw. Second SS wire also passed in same manner. Inferior ends of SS wires were crossed over and knotted to superior ends of opposite SS wire anteriorly in figure of eight manner and tensioned simultaneously on both the sides to achieve equal compression medially and laterally, knots were buried in the soft tissue ([Figure 2]B).[6]
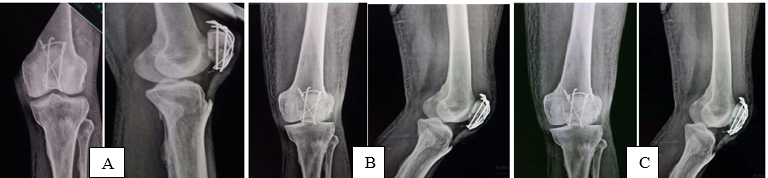
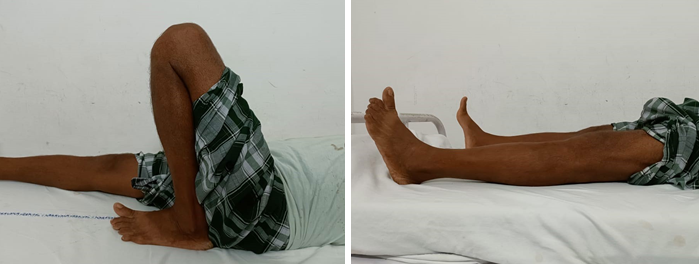
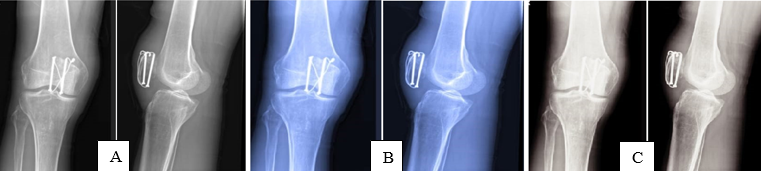
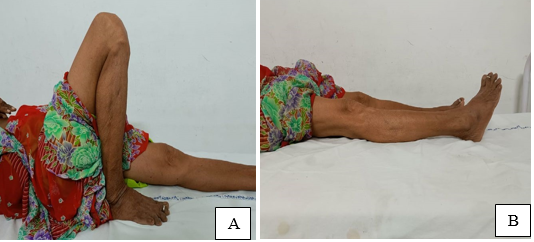
Patients were followed up at 1st, 3rd and 6th month after surgery and analyzed on clinical as shown in ([Figure 4] A,B) and ([Figure 6] A,B) and radiological parameters as shown in ([Figure 3] A,B and C) and ([Figure 5] A,B and C) The fracture union was defined when bridging callus was observed on a lateral radiograph. The final functional outcome was assessed using the WEST’S Criteria at 6th month.[8], [9]
Functional Scoring scale used (WEST’S criteria)[9]
Excellent:
Patient do not have any limitation of activities
No loss of flexion
No extensorlag
No subjective complaints
No quadriceps wasting or subsequent reduction in power
Good (1 or>1 criteria):
Moderate limitation of activity
Extensor lag of 5-10 degrees
Minimal wasting of quadriceps and power of Grade 4
Some subjective symptoms
Flexion loss not >30 degrees
Poor (1 or>1 criteria):
Marked limitation of activities with significant
Complaints of pain and weakness
Marked quadriceps wasting and power <3
Extensor lag>10 degrees
Flexion loss >30 degrees
We used appropriate statistical method like proportions, percentages, independent t test, Fischer's exact test for proportion and relevant graphs viz bar chart, line graph for evaluation of the outcome/results.
Sample size of estimation
Sample size is calculated using formula for difference between two means, with 5% level of significance and 80%power of the study.
Results
In our study, age of patients in the Cannulated cancellous screws group with mean age of 37.33+10.27 SD years. Patients in the Tension band wiring group with a mean age of 36.21±10.73 SD years which was statistically insignificant (p=0.773), ([Table 1]).
|
Age |
Cannulated Cancellous Screw N (%) |
Tension Band Wiring N (%) |
Total |
P - Value |
|
21 - 30 |
5 (33.3) |
5 (33.3) |
10 (33.3) |
|
|
31 - 40 |
5 (33.3) |
4 (26.7) |
9 (30) |
|
|
41 - 50 |
3 (20) |
5 (33.3) |
8 (26.7) |
|
|
51 - 60 |
2 (13.4) |
1 (6.7) |
3 (10) |
|
|
Total |
15 (100) |
15 (100) |
30 (100) |
0.772 (Independent t- test) |
|
Mean |
37.33 |
36.21 |
|
|
|
S.D |
10.27 |
10.73 |
|
Classification of transverse patella fractures were equally distributed, 34 C1 and 34 C2 is 1:1 in both Cannulated cancellous screws and Tension wiring groups ([Table 2]).
|
Classification |
Cannulated Cancellous Screw |
Tension Band Wiring |
|
34 C1 |
11 (73.3) |
11 (73.3) |
|
34 C2 |
4 (26.7) |
4 (26.7) |
All the fractures in both the study groups were united and the average time for the radiological union in Cannulated Cancellous Screws group with mean of 9.2±0.94 SD weeks and in Tension band wiring group with mean of 9.73±0.96 SD weeks with p- value of 0.137 measured using independent t test showed no statistical significance ([Table 3]).
|
Radiological Union |
Cannulated Cancellous Screw Mean (SD) |
Tension Band Wiring Mean (SD) |
P – Value |
|
Time for radiological union in weeks |
9.2(0.94) |
9.73(0.96) |
0.137 (Independent t -test) |
Between the two groups, the mean range of movements of knee after 6 months of fracture fixation showed a statistically insignificant difference with a p-value of 0.095. Maximum ROM recovered during the first six months after surgery. Extensor lag was not present in any of the patients ([Table 4]).
|
Mean Range of Movement |
Cannulated Cancellous Screw Mean (SD) |
Tension Band Wiring Mean (SD) |
P – Value |
|
Mean Range of Movement |
135 (9.06) |
129 (9.97) |
0.095 (Independent t-test) |
VAS Score was calculated at the end of 3 months and 6 months and showed a statistically insignificant difference between both the study groups with a p-value of 0.639 after 3 months and a p-value of 0.033 by the end of 6 months ([Table 5]).
|
VAS Score |
Cannulated Cancellous Screw |
Tension Band Wiring |
P - Value |
|
By the End of 3 Months |
2.73±1.22 |
2.93±1.09 |
0.639 |
|
By the End of 6 Months |
0.93±0.67 |
1.46±0.63 |
0.033 |
Among the complications in both study groups, anterior knee pain was noted in 1 patient in Cannulated cancellous screws(CCS) group and hardware prominence was seen in 3 patients in Tension band wiring(TBW) group and implant removal was needed in all 3 patients ([Table 6]).
|
Complications |
Cannulated Cancellous Screw N (%) |
Tension Band Wiring N (%) |
P - Value |
|
Anterior Knee Pain |
1 (6.7) |
0 |
0.045 (Chi-Square test) |
|
Hardware Prominence |
0 |
3 (20) |
By the end of 6 months functional outcome in Cannulated cancellous screws group were 66.7% Excellent, 26.6% Good and 6.7% Poor and in Tension band wiring group were 46.6% Excellent, 40% Good and 13.4% Poor. Although, the difference in Functional Outcome was statistically insignificant (p value= 0531), ([Table 7]).
|
Functional Outcome (WEST’S Score) |
Cannulated Cancellous Screw N (%) |
Tension Band Wiring N (%) |
Total |
P - Value |
|
Excellent |
10 (66.7) |
7 (46.6) |
17 (56.7) |
0.531 (Chi-Square test) |
|
Good |
4 (26.6) |
6 (40) |
10 (33.3) |
|
|
Poor |
1 (6.7) |
2 (13.4) |
3 (10) |
Discussion
Tension band wiring is one of the most popular technique for treating transverse fractures of patella, because of its ease of application and the probability of achieving union. However, it has some common complication like implant irritation, migration of k wires which affects the rehabilitation process which leads to pain and poor functional outcome. The k-wires in tension band wiring technique does not by itself generate compression force at fracture site. Rather the compression effects are provided by anterior tension band wire leading to maximum compression occurring at the anterior half of patellar surface than on the articular surface. The compression forces are not uniform throughout the fracture site.[3], [5], [10] Due to smooth geometry of k-wires, loosening of k-wire with time is more common with increased necessity of reoperation to remove hardware.[11], [12]
The cannulated cancellous screws on the other hand are more rigid as shown in cadaveric studies. Primary compression can be achieved by screws alone. Anterior tension band gives additional protection. As screw length is matched to patellar height, prominence of hardware with lesser incidence of surrounding soft
tissue irritation, pain and necessity for implant removal.[13], [14], [10]
In our study equal number of patients were treated in both groups (n=15 each) with the objective for evaluation of fracture union, clinical outcome and complications with a minimum follow up period of 6 months. All the fracture united by 9-11 weeks with statistical insignificance between the two groups. At final follow up, the average knee flexion was 135° in Cannulated Cancellous Screws group and 139° in Tension band wiring group. However, three patients in TBW group had k-wire migration/irritation which led to hardware removal. One patient in cannulated cancellous screws(CCS) group developed anterior knee pain which might be because of tender and adherent operative scar. This patient with anterior knee pain had no evidence of radiographic arthritis in their final follow-up x-ray.
Tan et al in a retrospective study compared cannulated screws and tension band wiring. In his study 11.5% in tension band wiring(TBW) group had painful hardware and implant migration-related complication but no hardware-related complications were found in cannulated screws group. In his study mean knee ROM on 6th month was 139.2° in Cannulated Cancellous Screws(CCS) group & 135° in Tension band wiring(TBW) group.[15]
Tian et al., in a retrospective study compared cannulated screws with cable and Tension band wiring technique for the treatment of transverse patellar fracture. In his study found that 15% in Tension band wiring(TBW) group had painful hardware relating to implant migration. In our study 20% of patients in Tension band wiring(TBW) group had similar problems.[16] In Tian et al.,study 3 patients had got fixation failure then underwent reoperation. In present study, Tension band wiring(TBW) group we didn’t observe any fixation failure, but sample size in present study was not significant to compare with above study.[16]
Hoshino et al in a retrospective cohort study compared complications in Cannulated cancellous screws(CCS) and Tension band wiring(TBW) comprising study population of 315(70%) and 133(30%) respectively. In his study had fixation failure of 3.5% in Tension band wiring(TBW) group and 7.5% in cannulated screw group.[17] In our study we haven’t experienced any fixation failures, since we performed study in single institution with small population, unlike the above study. In Hoshino et al study symptomatic hardware was found to be 36% in Tension band wiring(TBW) group and 22.6% in cannulated screw group. In present study no symptomatic hardware was found in cannulated screws group, 20% in Tension band wiring(TBW) group, however the limitation of present study being smaller sample size.[17]
Chokkarapu Ramu et al., study showed the reoperation rate was 0% (0/10 patients) in the Cannulated cancellous screws(CCS) group and 10% (1/10 patients) in the tension band wiring(TBW) group and also showed patient treated with Cannulated cancellous screws(CCS) had good pain scores and ROM at early follow up period (up to 6 months), there were no differences noted in these measures at the final 6 months follow-up.[18] But in our study pain scores and range of motion(ROM) were similar even at 6 months in both Cannulated Cancellous Screws(CCS) and Tension band wiring(TBW) groups.
Limitations
Our study has several limitations like small sample size, short period of follow up and convenient sampling. Cannulated Cancellous Screws technique being a relatively new method, there is need for longer period follow up, large study population in order to substantiate the safety and biomechanical advantage of this method.
Conclusion
Hence, we concluded that intraarticular introduction of Plateletrichplasma in Periarthritisshoulder showed reduction in the intensity of pain, increase in angle of movements of shoulder joint and improvement in ability of carrying daily activities without restrictions which the patients were not able to do before.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted after taking approval from the Institution Ethics Committee with ref. no. NMC/Adm/Ethics/approval/091/2021.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
None.
References
- Fox A, Wanivenhaus F, Rodeo S. The basic science of the patella: structure, composition, and function. J Knee Surg. 2012;25(2):127-41. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P, Court-Brown C, Vedel J, Vistrup S, Elsoe R. Incidence and epidemiology of patellar fractures. Orthopedics. 2016;39(6):1154-8. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer K, Moed B. Patellar fractures: contemporary approach to treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1997;5(6):323-31. [Google Scholar]
- Hung L, Chan K, Chow Y, Leung P. Fractured patella: operative treatment using the tension band principle. Injury. 1985;16(5):343-7. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter J, Kasman R, Patel N, Lee M, Goldstein S. Biomechanical evaluation of current patella fracture fixation techniques. J Orthop Trauma. 1997;11(5):351-6. [Google Scholar]
- Chang S, Ji X. Open reduction and internal fixation of displaced patella inferior pole fractures with anterior tension band wiring through cannulated screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2011;25(6):366-70. [Google Scholar]
- Adjal J, Ban I. Patella fractures treated with suture tension band fixation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1). [Google Scholar]
- Tegner Y, Lysholm J. Rating systems in the evaluation of knee ligament injuries. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;198:43-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsou A, Vallianatos P, Piskopakis N, Maheras S. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction by over-the-top repair combined with popliteus tendon plasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990;72(3):398-404. [Google Scholar]
- Zderic I, Stoffel K, Sommer C, Höntzsch D, Gueorguiev B. Biomechanical evaluation of the tension band wiring principle. A comparison between two different techniques for transverse patella fracture fixation. Injury. 2017;48(8):1749-57. [Google Scholar]
- Fortis A, Milis Z, Kostopoulos V, Tsantzalis S, Kormas P, Tzinieris N. Experimental investigation of the tension band in fractures of the patella. Injury. 2002;33(6):489-93. [Google Scholar]
- Luna-Pizarro D, Amato D, Arellano F, Hernández A, López-Rojas P. Comparison of a technique using a new percutaneous osteosynthesis device with conventional open surgery for displaced patella fractures in a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(8):529-35. [Google Scholar]
- Boström �. Fracture of the patella: a study of 422 patellar fractures. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1972;143:1-80. [Google Scholar]
- Berg E. Open reduction internal fixation of displaced transverse patella fractures with figure-eight wiring through parallel cannulated compression screws. J Orthop trauma. 1997;11(8):573-6. [Google Scholar]
- Tan H, Dai P, Yuan Y. Clinical results of treatment using a modified K-wire tension band versus a cannulated screw tension band in transverse patella fractures: a strobe-compliant retrospective observational study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(40). [Google Scholar]
- Tian Y, Zhou F, Ji H, Zhang Z, Guo Y. Cannulated screw and cable are superior to modified tension band in the treatment of transverse patella fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(12):3429-35. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino C, Tran W, Tiberi J, Black M, Li B, Gold S. Complications following tension-band fixation of patellar fractures with cannulated screws compared with Kirschner wires. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(7):653-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ramu C, KR, BA, BK, Shanmuga P. Management of patella fractures with different modalities. Int J Res Orthop. 2019;5(3):422-6. [Google Scholar]
How to Cite This Article
Vancouver
Jyothsna RV, Ravindran B, Yadav VR. A prospective study to compare the outcome of patellar fractures treated with tension band wiring versus cannulated cancellous screws fixation [Internet]. Indian J Orthop Surg. 2024 [cited 2025 Nov 04];10(4):329-334. Available from: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijos.2024.054
APA
Jyothsna, R. V., Ravindran, B., Yadav, V. R. (2024). A prospective study to compare the outcome of patellar fractures treated with tension band wiring versus cannulated cancellous screws fixation. Indian J Orthop Surg, 10(4), 329-334. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijos.2024.054
MLA
Jyothsna, Rachuru Venkata, Ravindran, Biju, Yadav, Vinod Ramlal. "A prospective study to compare the outcome of patellar fractures treated with tension band wiring versus cannulated cancellous screws fixation." Indian J Orthop Surg, vol. 10, no. 4, 2024, pp. 329-334. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijos.2024.054
Chicago
Jyothsna, R. V., Ravindran, B., Yadav, V. R.. "A prospective study to compare the outcome of patellar fractures treated with tension band wiring versus cannulated cancellous screws fixation." Indian J Orthop Surg 10, no. 4 (2024): 329-334. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijos.2024.054
